
Whenever the state of an enabled digital input changes, an event will be sent to the analysis PC.ĭigital outputs allow users to output events to external devices.
Controller Area Network Wikipedia article – Wikipedia.Applications other than this, such as reading from a large memory device, would not use CAN. Protocol overhead – The CAN protocol has a moderate amount of overhead (strict message formatting, CRC checking, bit-stuffing, etc.) and is more complicated than other protocols such as I 2C and SPI.ĬAN is well-suited for connecting many devices that have small amounts of data to share with each other at low data rates.Small data transfers – data frames can only carry 8 bytes, so CAN is not good for large data transfers.This is not good for high-bandwidth applications. Low-bandwidth – CAN supports a maximum data rate of 1 Mbps.Buses can be very long – On the order of miles and kilometers.Many nodes can be connected on the same bus – CAN 2.0B defines identifiers as 29 bits, providing over 500,000 unique codes.Configuration flexibility – Nodes can be added to and removed from the bus without modifying other nodes.Robust – High performance, even in difficult electrical environments.High reliability – Achieved through built-in error checking.Automatic arbitration – Based on message identifier.Automatic prioritization of messages – Based on message identifier.Multi-master – All nodes can transmit and receive messages.1.1.3 CAN Features and BenefitsĬAN has many important features and benefits, including: For more information about the Komodo interfaces compatibilities, please refer to Section 2.
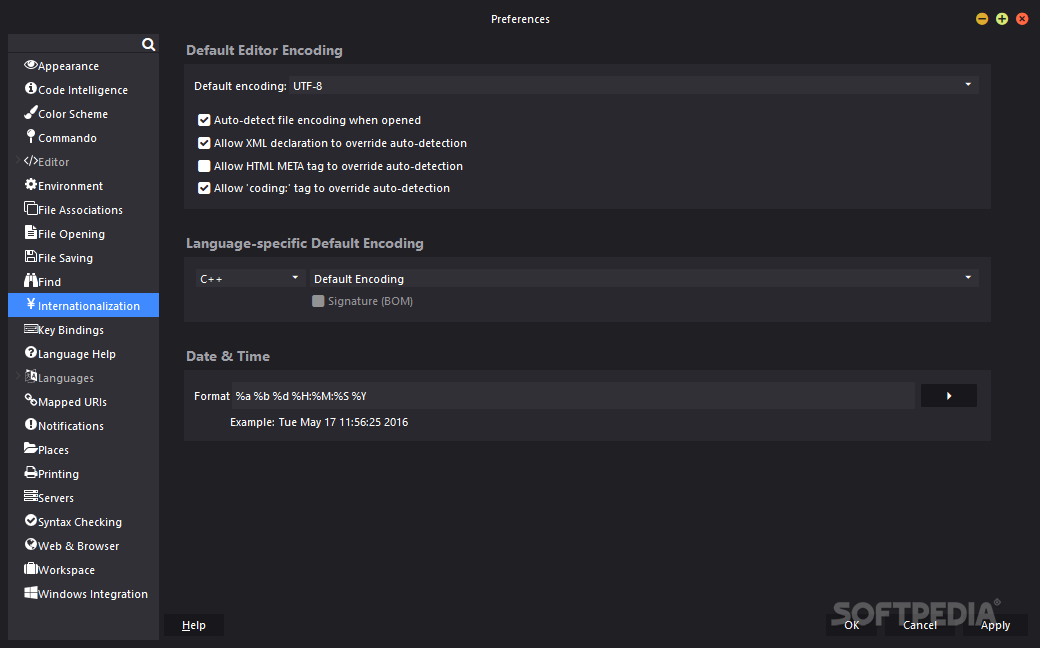
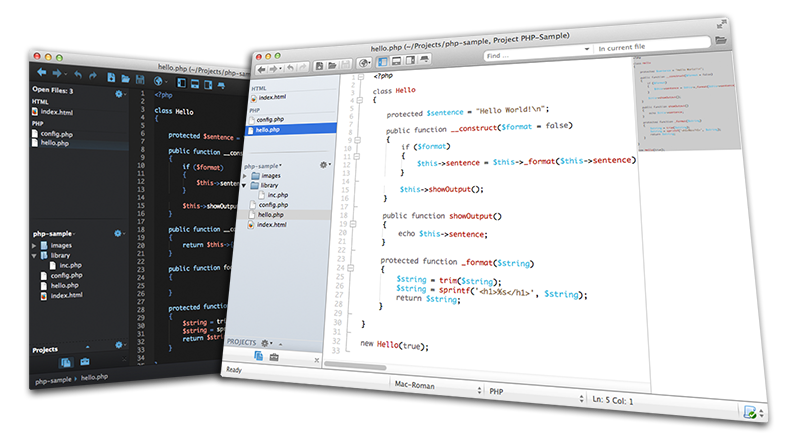
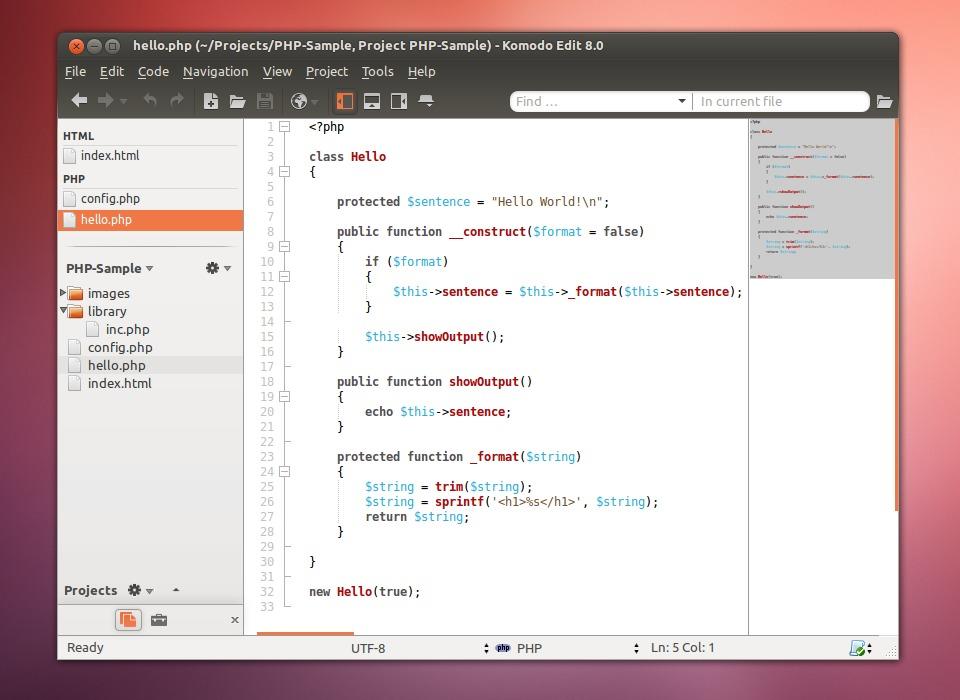
Komodo edit 10 manual iso#
1.1.2 CAN Theory of OperationĬAN allows multiple devices (referred to as "nodes") to connect to each other on a single bus, as shown in Figure 1. The most common CAN physical layer standard is ISO 11898-1, but others are also used. However, operating at low data rates makes CAN quite robust to noise and allows buses to span long distances.ĬAN was originally designed for use in automobiles, but has also become popular in low-bandwidth industrial applications such as controlling assembly line machines.Īlthough Boschs CAN specification does not define standard CAN voltages or connector interfaces, standards organizations have defined multiple physical standards. CAN is not a fast bus by today's standards, with a maximum data rate of only 1 Megabit per second.
It is optimized for sending small amounts of data between multiple nodes.
Komodo edit 10 manual serial#
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial bus protocol created in the mid-1980s by the German company Bosch.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
